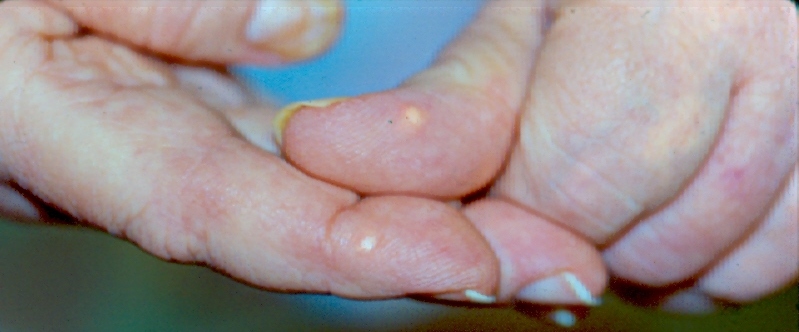
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is a typical intricacy of hematologic malignancies. Certain neuropathies might be identified with the basic harm itself, particularly in patients with different myeloma and Waldenström macroglobulinemia, which are related with paraproteinemic fringe neuropathy.
Be that as it may, fringe neuropathy most generally happens because of the restorative routine used to treat malignancies. Neurotoxic symptoms can results from numerous treatments much of the time used to treat various myeloma, lymphomas, and leukemias, including proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory medications, and vinca-alkaloids.
At the point when fringe neuropathy happens during treatment, portion decrease or even treatment end might be required, which can unfavorably influence tolerant results. Manifestations may likewise continue after treatment closes, which contrarily influences personal satisfaction.
Personal satisfaction after treatment has gotten progressively significant as endurance paces of patients with hematologic malignancies consistently keep on rising. Along these lines, noticed the writers of an audit article distributed in Blood Reviews, analysts need to build the accentuation on treatment-remaining symptoms to guarantee that patients can appreciate a high caliber of life once they have finished dynamic treatment.
Right now, scientists gave an update of neurotoxic medicines that are at present utilized in hematologic malignancies, the hidden instruments prompting fringe neuropathy in the clinical setting, and treatment and rehabilitative procedures for patients who are influenced by this confusion.
“Peripheral neuropathy is a major dose-limiting toxicity of many treatments used for hematologic malignancies that can continue to [influence] patient quality of life post-treatment,” said Susanna B Park, PhD, associate professor of physiology at the School of Medical Sciences at the University of Sydney in Australia, in an interview with Hematology Advisor. “Consequently, special attention to the development and severity of peripheral neuropathy is needed. Close monitoring of peripheral neuropathy symptoms with validated measures and prompt action according to dose modification protocols may help prevent severe long-term neuropathy.”
Medications Associated with Peripheral Neuropathy
Fringe neuropathy is much of the time found in patients with numerous myeloma as an outcome of both the ailment itself and treatment for it. Regular regimens incorporate immunomodulatory specialists (thalidomide, lenalidomide, and pomalidomide) and proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib and carfilzomib), which are all related with unfavorable occasions, including myelosuppression, thrombosis, gastrointestinal occasions, and fringe neuropathy.
Bortezomib is the first proteasome inhibitor that got administrative endorsement and is utilized for both recently analyzed and backslid or unmanageable numerous myeloma. Fringe neuropathy is a typical unfavorable occasion, and portion decrease, delay, or even end of treatment is frequently required when this specialist is utilized. A few information propose that giving dexamethasone on a similar day as bortezomib may bring about less extreme fringe neuropathy, contrasted and different sorts of dexamethasone dosing plans (counting week by week dexamethasone).
Second-age proteasome inhibitors, for example, carfilzomib and ixazomib have gotten accessible as elective treatment choices, and one examination indicated that carfilzomib decreased generally speaking neuropathy contrasted and bortezomib (6% versus 32%). Ixazomib, the first orally directed proteasome inhibitor, has likewise indicated no expansion in neuropathy when contrasted and lenalidomide and dexamethasone. An ongoing stage 2 examination found that 13% of patients treated with ixazomib created fringe neuropathy of any evaluation.
Immunomodulatory specialists are likewise normally used to treat numerous myeloma. A high pace of fringe neuropathy has been accounted for with thalidomide use and has been seen in up to 75% of patients accepting treatment, despite the fact that portions utilized across clinical preliminaries fluctuate.
As anyone might expect, hazard for fringe neuropathy is expanded when thalidomide is joined with bortezomib, and stage 3 investigations have demonstrated a higher occurrence of by and large neuropathy (60% versus 13%) and serious neuropathy (14% versus 5%) with this routine contrasted and thalidomide utilized alone during acceptance. Second-age immunomodulators lenalidomide and pomalidomide were created to build viability and limit danger and have shown essentially less neurotoxicity during both enlistment and upkeep treatment.